Labral Tear Shoulder Explained: Early Signs and How to Heal Faster
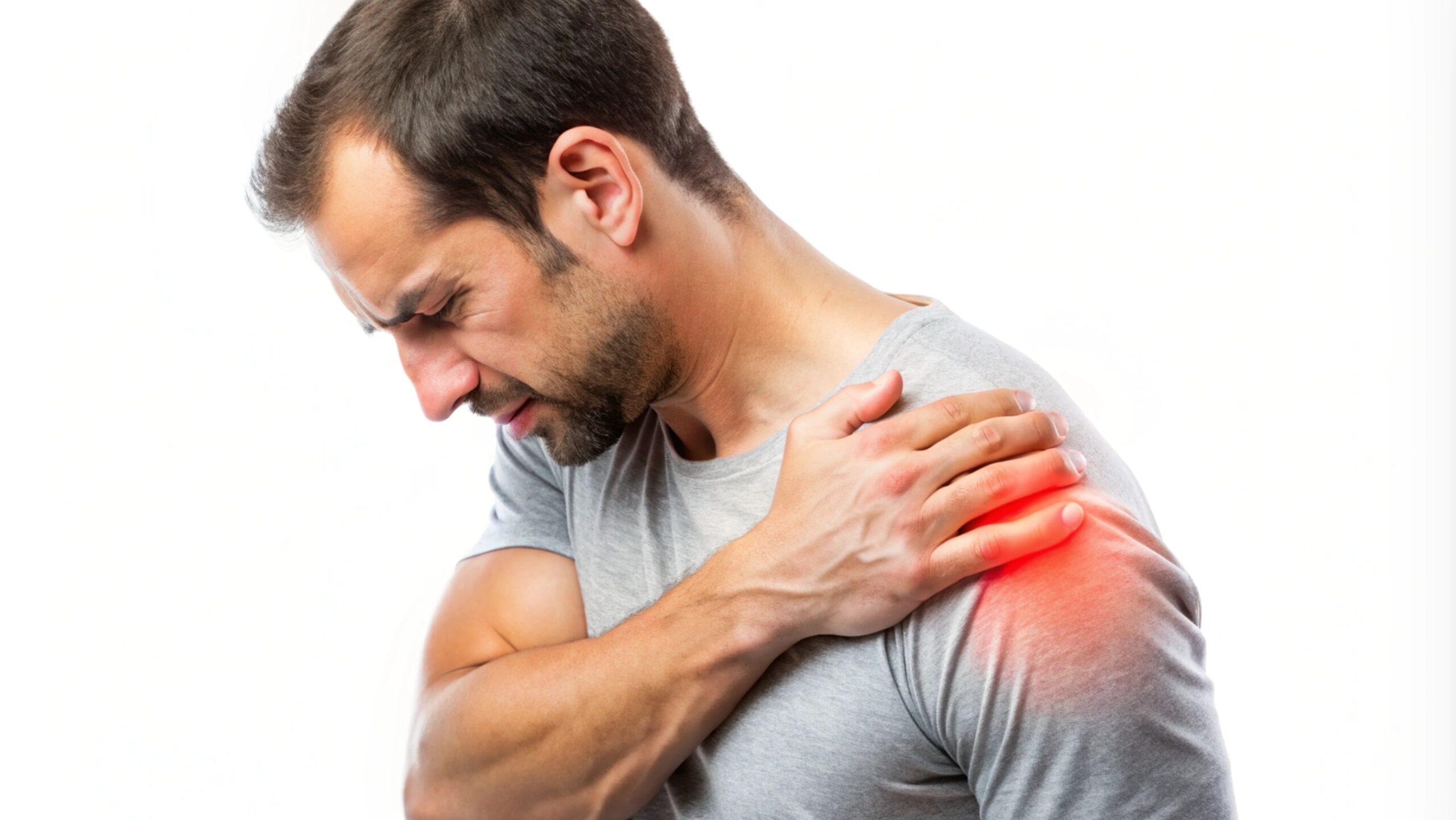
Many people in India experience shoulder pain without knowing why it keeps returning, especially during simple tasks like reaching overhead, lifting a light object, or even sleeping on one side.
Sometimes the pain travels down the upper arm bone, sometimes the shoulder blade feels stiff, and sometimes the joint feels loose or unstable during routine work. When these signs persist for weeks, the underlying cause could be a labral tear in the shoulder, a condition that affects the soft ring of cartilage called the shoulder labrum.
This ring forms a protective cushion inside the shoulder joint, which is a classic ball-and-socket joint. The round top of the arm bone fits into the shoulder socket, and the shoulder labrum keeps it stable.
When the labrum tears, the joint becomes unstable, painful, and difficult to move. Many cases worsen because people ignore early signals, thinking it is a simple strain. But the labrum plays a vital role in shoulder stability, and any injury to this structure needs timely attention. Let’s break down every part of this injury.
What is a Labral Tear Shoulder?
Before moving into deeper sections, let us look at the basics.
A labral tear in the shoulder occurs when the cartilage ring that holds the arm bone in place is damaged. It may happen due to sports, a fall, sudden pulling, or repetitive overhead motions. The damage creates shoulder pain, weakness, instability, and difficulty lifting the arm.
The tear may involve the biceps tendon, which is firmly attached to the superior labrum. Injuries involving this part are called SLAP tears or SLAP lesions, which means” superior labrum anterior and posterior”. Some people experience a Bankart tear, which causes shoulder instability and recurrent dislocations. Each pattern has a different severity level, but all need proper management.
How the Shoulder Labrum Works
Common Signs Your Hip Might Be Impinged
Why the Labrum Gets Injured Easily
The shoulder has a wide range of motion, which creates flexibility but reduces its natural stability. So, the labrum often suffers from:
- Repetitive throwing
- Overhead motions
- Sudden external rotation
- Traumatic injury
- Falls or direct impact
Overhead athletes, such as bowlers, volleyball players, weightlifters, and swimmers, face a higher risk.
Types of Labral Tears and How They Differ
Major Types of Labral Tears and Their Characteristics
| Tear Type | Primary Area Involved | Typical Causes | Effect on Shoulder Stability |
| SLAP Tear | Superior labrum, near the biceps tendon | Repetitive throwing, overhead motion | Pain during lifting and rotation |
| Bankart Tear | Front-bottom portion of the labrum | Shoulder dislocation, traumatic injury | High chance of recurrent dislocations |
| Posterior Instability Tear | Back side of the labrum | Contact sports, heavy pushing | Instability and pain during pushing |
| Degenerative Labrum Tear | Soft tissues wear out | Ageing, long-term strain | Chronic pain and reduced strength |
| Torn Flap Tear | Loose, torn flap floating inside the joint | Sudden twisting or lifting | Catching or locking sensation |
This table helps you understand how different regions of the shoulder labrum contribute to specific symptoms and how each tear affects long-term shoulder health.
Early Signs of a Labral Tear in the Shoulder You Should Pay Attention To
Main Symptoms
You may notice:
- Shoulder pain while lifting your arm
- A clicking or locking sensation when moving
- Feeling that the shoulder may slip out
- Weakness while performing overhead motions
- Pain during rotation
- A dull aching pain deep inside the joint
- Difficulty sleeping on one side
These signs appear because a torn labrum disrupts shoulder stability and irritates soft tissues.
What a Torn Labrum Feels Like During Daily Tasks
Causes Behind Shoulder Labral Tears
Non-Surgical Recovery and Treatment
Repetitive Throwing Movements
Overuse and Age-Related Changes
Heavy Lifting and Poor Form
Shoulder Instability and Previous Injuries
How to Take Care of Your Hip Joint

Physical Examination
Doctors check:
- Pain location
- Muscle strength
- Stability during rotation
- Specific directions of pain
- Reaction of the shoulder during pressure
Several physical tests reproduce symptoms to confirm the tear.
Imaging Tests
The most accurate imaging tools are:
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Magnetic resonance imaging MRI with contrast for deeper detail
- Shoulder arthroscopy (also used for treatment)
MRI findings show tear patterns, soft tissue damage, and biceps tendon involvement.
Treatment Options for Labral Tears
Nonsurgical Treatment Options
These treatments help many patients avoid surgery:
- Rest and physical therapy
- AAnti-inflammatorymedications
- Pain medication
- Corticosteroid injections
- Limited overhead motions
- Avoiding further injury
Physical therapy focuses on strengthening rotator cuff muscles, improving posture, and increasing stability.
Surgical Treatment Options
Some injuries do not respond to conservative treatment. These require:
- Labrum repair
- Arthroscopic techniques
- Use of small incisions
- Shoulder labral tear surgery for unstable joints
- Labrum surgery using suture anchors
- Arthroscopic surgery for flap removal or repair
Surgeons use small surgical instruments to repair torn labrum sections.
Rehabilitation and Recovery After a Labrum Tear
What Happens During Rehab
Rehabilitation involves:
- Controlled range of motion exercises
- Strengthening rotator cuff tendons
- Mobility and stretching
- Shoulder stability training
- Gradual return to overhead activity
Importance of a Physical Therapist
Avoiding Further Injury During Recovery
Patients must avoid:
- Heavy lifting
- Repetitive throwing
- Overhead motions
- Sudden external rotation
These actions delay healing.
How to Heal Faster and Reduce Pain Naturally
Improve Muscle Balance
Manage Pain Without Excessive Medication
Maintain Flexible Soft Tissues
Heal Your Shoulder Faster With Expert Care
A labral tear in the shoulder can affect movement, strength, and daily comfort. Early diagnosis, correct imaging, and timely treatment help prevent further damage. Whether it is a SLAP tear or a degenerative tear, the proper guidance creates a safe path to recovery. If you feel clicking, sharp pain, locking, weakness, or instability, do not delay.
To book a personalised recovery plan, you can schedule an appointment at SRM Global Hospitals. Their specialists help you heal safely and regain shoulder function with structured treatment and advanced care.