Knee Cartilage Damage Explained: Early Signs You Shouldn’t Ignore
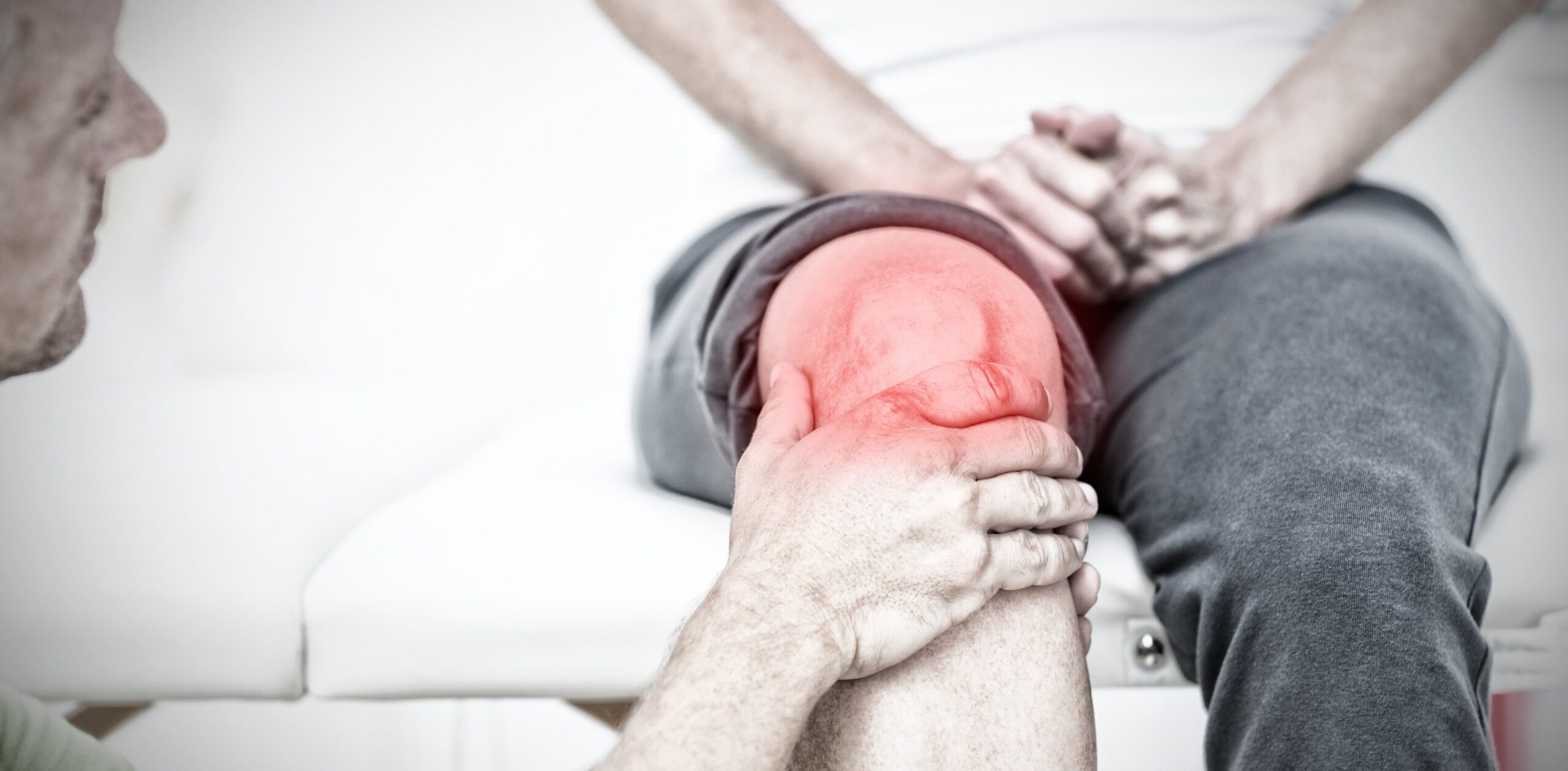
Ever heard a strange popping sound from your knee or felt pain when bending or turning it? Many Indians ignore these early signs, thinking they are just tired or aging. But in many cases, this could be an early warning of knee cartilage damage, which can cause joint pain, an issue that affects more people than we realise.
If not treated early, it can lead to reduced mobility, long-term knee pain, and even severe damage that might need surgery. This guide explains what knee cartilage damage is, including conditions such as knee osteoarthritis, how to recognize early signs, and the treatment options available in India, ranging from simple rest and therapy to advanced surgical procedures.
What Is Knee Cartilage and Why Is It Important?
Cartilage is a smooth, rubber-like tissue that covers the ends of bones in the knee joint. Cartilage is a smooth, rubber-like tissue that covers the ends of bones in the knee joint and contains cartilage cells. It acts as a cushion, reducing friction as your thigh and shin bones move. It also supports a range of motion and smooth movement.
When this cartilage wears down or gets damaged, bones start rubbing against each other. When this cartilage wears down or gets damaged, it exposes the underlying bone, leading to knee pain, stiffness, and swelling. Unlike skin or muscle, cartilage doesn’t heal easily because it has very little blood supply.
That’s why early treatment is so necessary.
How Knee Cartilage Gets Damaged
Main Causes of Cartilage Damage
- Wear and tear over time from walking, climbing stairs, or squatting
- Sudden trauma from sports or accidents
- Improper technique during lifting or gym workouts
- High-impact sports like cricket, football, or basketball
- Age-related degeneration of soft tissues
- Lack of blood supply, which limits natural healing
Even something as simple as squatting with poor posture can slowly weaken your cartilage.
Common Symptoms of Knee Cartilage Damage
Not all knee injuries feel the same. But these symptoms usually show up when cartilage damage begins:
- Knee pain during or after physical activity
- Swelling around the knee joint
- Stiffness, especially in the morning
- Grinding or popping sound while moving
- Feeling like your knee is locking or getting stuck
- Weakness while walking or climbing stairs
- Sharp pain while turning or squatting
- A sense that your injured knee might give way
If you feel these symptoms for more than a few days, consult an orthopaedic surgeon or physiotherapist.
Types of Knee Cartilage Injuries
Different injuries affect different layers of the cartilage or nearby tissues, such as the meniscus, and may require different surgical techniques.
| Type of Injury | Description | Common Among |
| Cartilage Defect | Minor, localised damage due to impact | Sports injuries, accidental falls |
| Articular Cartilage Damage | Smooth surface layer damage | Seniors, arthritis patients |
| Meniscus Tear | Tear in the cushioning pad between bones | Rotational injuries, athletes |
| Osteochondral Injury | Damage that includes both cartilage and bone | Road accidents, high-impact falls |
| Loose Cartilage Fragments | Broken pieces floating in the joint | Advanced degeneration cases |
Each condition needs a different treatment approach — from physical therapy to cartilage surgery or knee cartilage replacement.
How Doctors Diagnose Knee Cartilage Damage
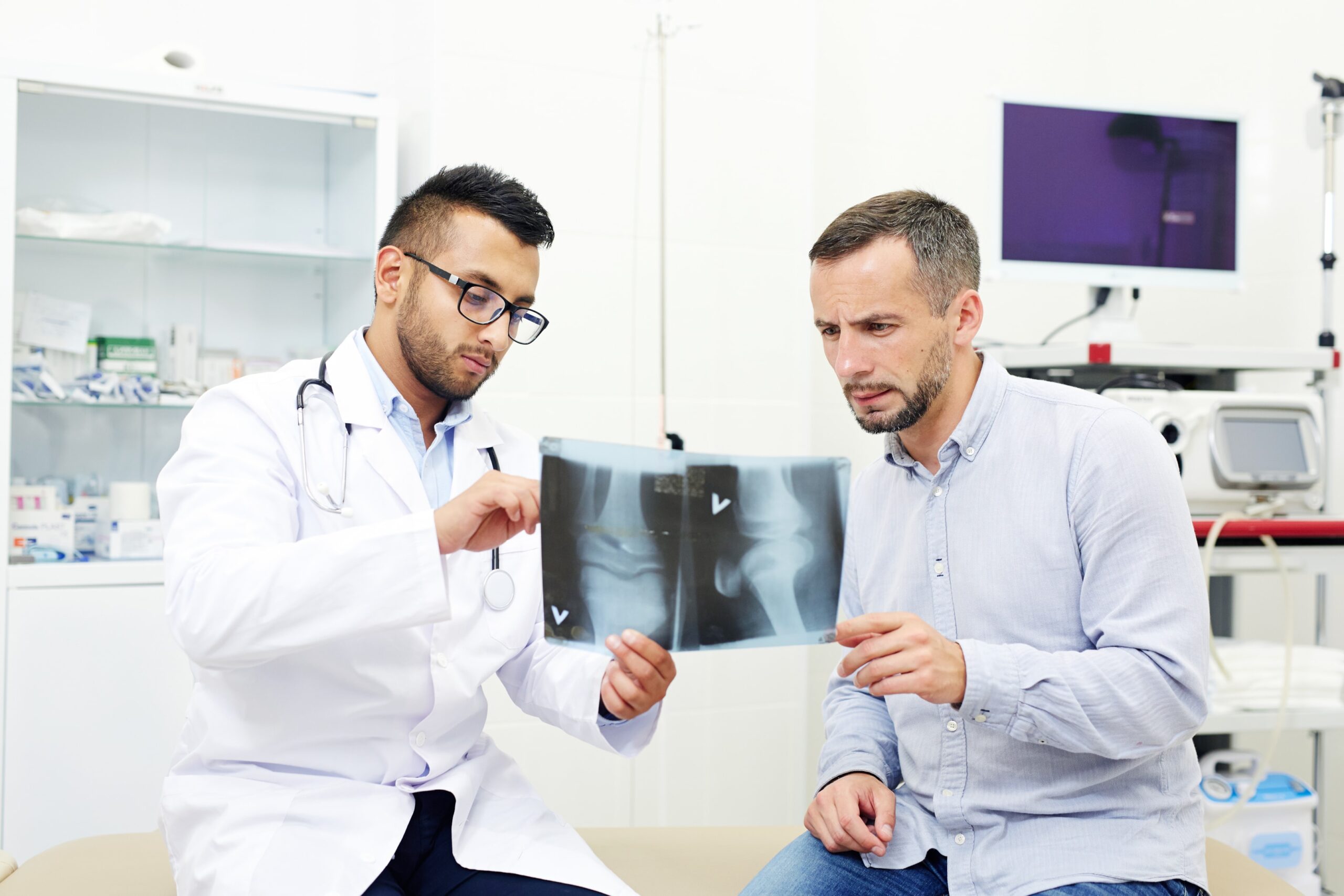
Physical Examination
They’ll check for various signs and may evaluate the presence of growth factors :
- Location of swelling
- Knee movement and flexibility
- Pain during bending and walking
Imaging Tests
- X-ray: To rule out bone fractures
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Gives a full view of cartilage layers
- Arthroscopy: A small camera is inserted to check the damage directly
Early diagnosis improves your chance of healing without surgery.
Treatment Options for Knee Cartilage Damage in India
Non-Surgical Options
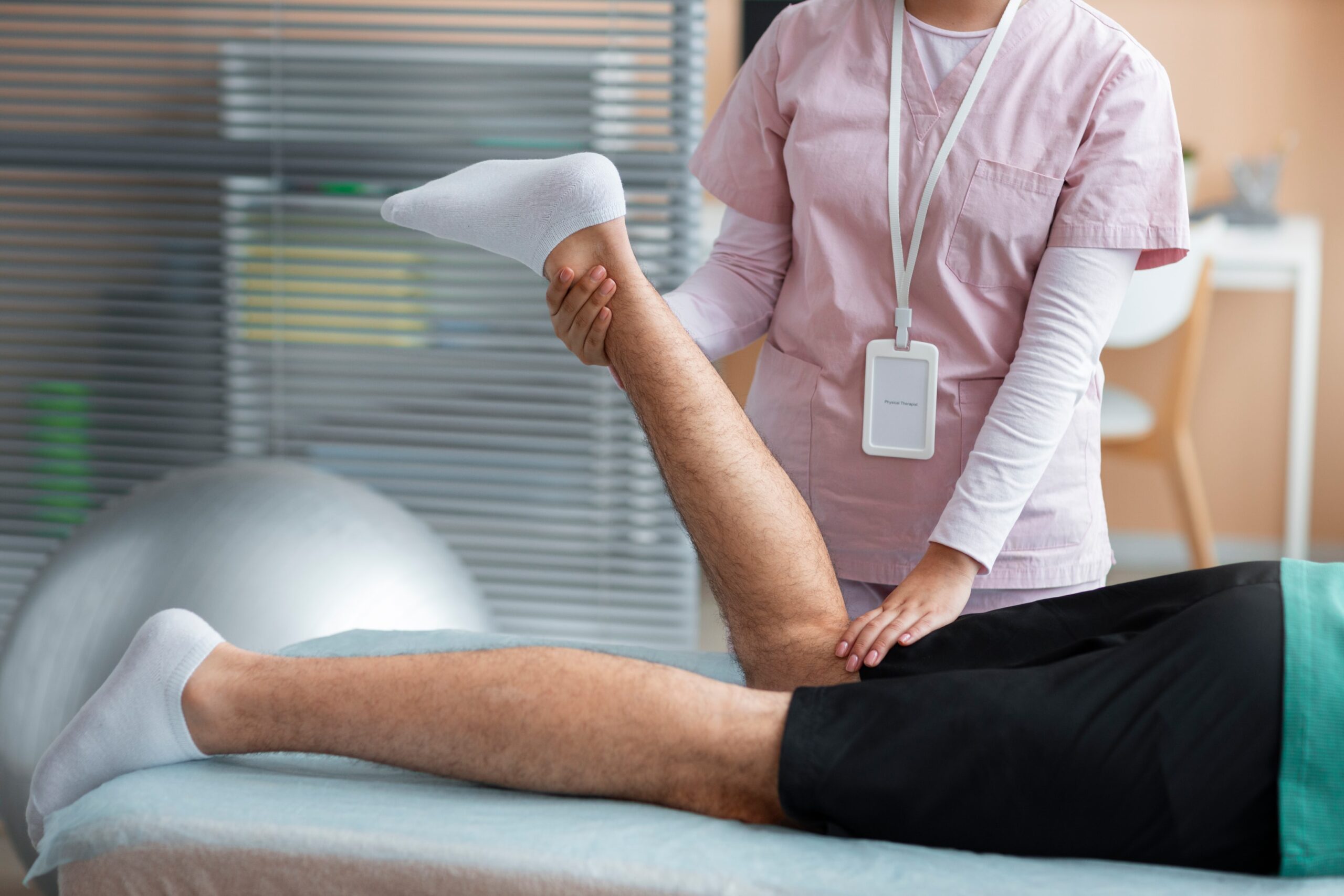

- Physical therapy: Builds supporting muscles and restores movement
- Anti-inflammatory drugs: Reduce pain and swelling
- PRP therapy: Platelet-rich plasma injections to promote healing
- Stem cell therapy: In some cases, it helps regrow damaged meniscus tissue
- Low-impact exercises: Walking, swimming, cycling, to maintain joint strength
- Knee braces: Support the joint during recovery
Surgical Procedures
If the cartilage is severely damaged:
- Arthroscopic surgery: Removes or repairs the tear
- Osteochondral autograft transplantation (OATS): Healthy cartilage is taken from a non-weight-bearing area and placed in the damaged zone
- Autologous chondrocyte implantation (ACI): Cells are collected, grown in a lab, then implanted into the knee
- Osteochondral allograft transplantation: Cartilage from a donor is used
- Mosaicplasty: Small cartilage plugs are inserted like a mosaic
Doctors choose the right method based on age, health, tear size, and lifestyle.
When to Consider Knee Cartilage Replacement
If all else fails, and the knee is too damaged:
- Knee cartilage replacement or partial joint replacement may be advised
- Usually needed in cases of:
- Severe degenerative meniscal tears
- Unbearable pain even after therapy
- Failed previous surgeries
- Knee locking or joint deformities
Consult with your orthopaedic doctor to check if this is right for you.
Recovery and Rehabilitation Tips for Faster Healing
Tips to Heal Faster
- Follow your rehabilitation exercises daily
- Avoid high-impact sports until the knee heals
- Use a knee support when walking or climbing
- Apply ice to reduce knee swelling
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce pressure on your affected knee
- Eat foods rich in collagen, protein, and anti-inflammatory nutrients
Healing time varies from 6 weeks to 6 months, depending on the treatment and consistency.
When to Visit SRM Global Hospitals
If your pain doesn’t go away in a few days or if you notice signs such as locking, swelling, or sharp pain, it’s time to act. At SRM Global Hospitals, specialists offer expert diagnosis, imaging, and tailored treatment plans.
Our experienced orthopaedic surgeons, advanced facilities, and dedicated physical therapy team ensure the best care, including assessment of blood vessels, from diagnosis to recovery.
Don’t let damaged cartilage ruin your active life. Visit SRM Global Hospitals for proper treatment, avoid further damage, and regain your strength step by step.