Comprehensive Guide to Labral Tear Shoulder: Symptoms and Treatments
Shoulder pain can stop you from doing even the simplest tasks like lifting a bag, combing your hair, or playing cricket with your children. Many people mistake this pain for muscle strain or tiredness, but sometimes the real issue is much deeper inside the shoulder joint. One of the hidden problems that cause nagging pain and weakness is a labral tear shoulder.
A labral tear can affect athletes, workers, homemakers, and even youngsters who love sports. Because the shoulder is a ball and socket joint that gives wide range of motion, injuries here can be tricky.
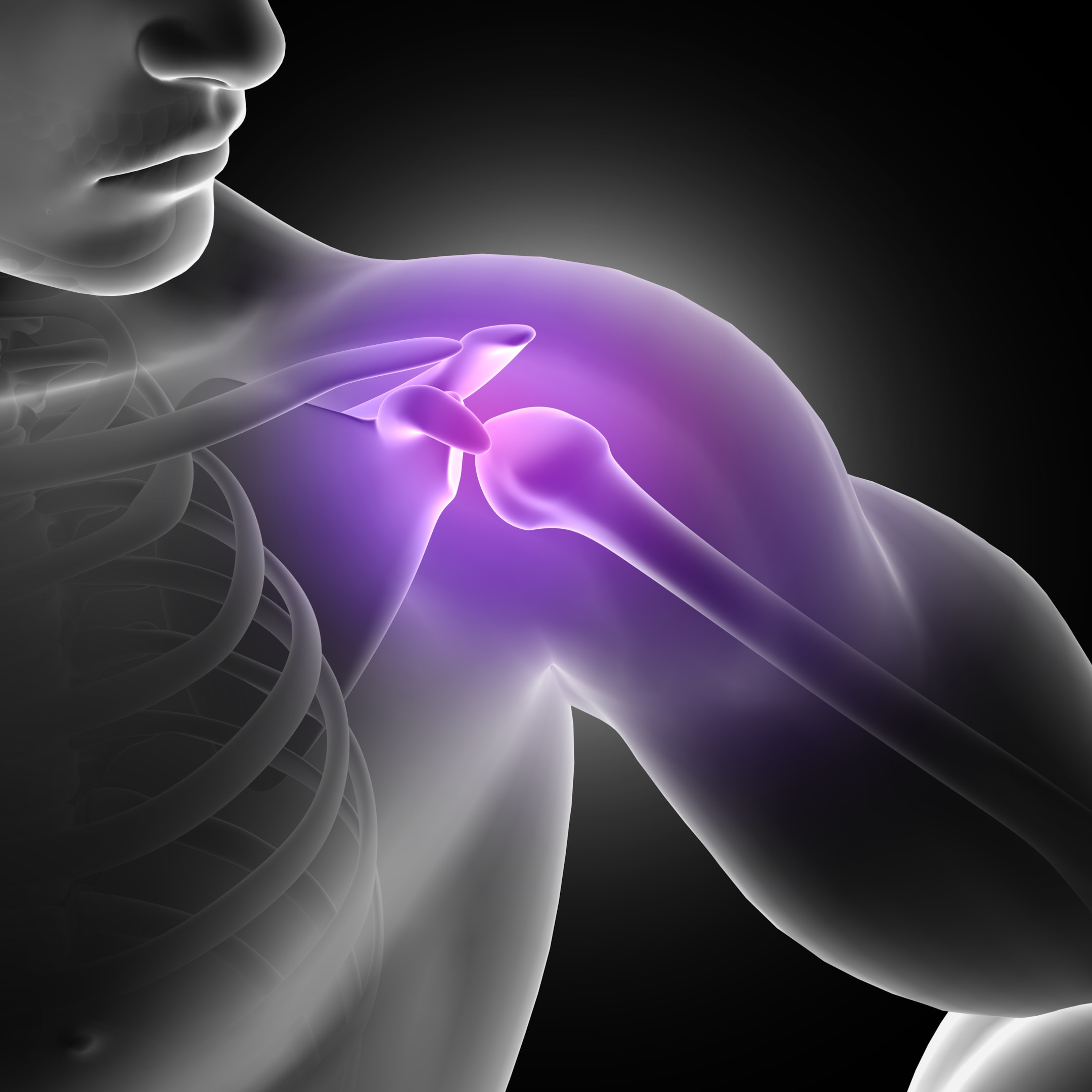
The labrum, which is a ring of cartilage, keeps the humeral head (the top of the upper arm bone) stable in the shoulder socket. When this labrum tears, either because of acute trauma or repetitive movements, the shoulder becomes unstable and painful.
What is a Labral Tear in the Shoulder?
The shoulder labrum is a tough ring of cartilage that lines and strengthens the shoulder socket. It acts like a cushion and stabiliser. It is also the attachment site where the biceps tendon connects to the shoulder.
When a labrum tear happens, it means this ring has been damaged. The tear may be small or large. Small tears can cause mild discomfort, but severe tears lead to shoulder instability, weakness, and even repeated shoulder dislocation. Doctors classify these tears into many types such as superior labral tear, anterior labral tear shoulder, and bankart tear. Each type affects movement in different ways.
Think of the labrum as the “seat belt” of the shoulder. If the seat belt is cut or damaged, the joint becomes unsafe. That is exactly what happens in a shoulder labrum tear.
Causes of Labral Tears
Labral tears rarely happen without a reason. They often result from direct injury or constant stress on the shoulder joint. Let us look at some of the most common causes.
Sports and Repetitive Motion
Athletes are at higher risk. Baseball pitchers, weightlifters doing bench press, and swimmers often develop tears because they use overhead motions again and again. Playing sports that require throwing also puts extra pressure on the labrum.
Shoulder Dislocation
When the shoulder slips out of its socket, the labrum often gets damaged. A torn shoulder labrum is very common after shoulder dislocation, especially in young and active people.
Direct Blow or Accident
A sudden direct blow, fall on an outstretched arm, or road accident may tear the labrum. Such injury causes sudden pain and limits shoulder function immediately.
Age and Wear
With age, the labrum loses strength. Small tear occurs naturally over time due to daily physical activity. People above 40 may have a labrum tear without any major accident.
Heavy Lifting and Work Stress
Jobs or workouts that demand lifting heavy objects repeatedly also damage the labrum. Overuse weakens the shoulder ligaments and leads to a labral tear in the shoulder.
Risk Factors of Labral Tears
Not everyone gets a labral tear. Certain factors make some people more vulnerable.
Younger Athletes
Younger athletes who train hard in cricket, volleyball, or baseball are at higher risk. Their labrums are repeatedly strained from fast and strong overhead throws.
Overhead Motion Jobs
Workers who frequently reach above their heads, like painters or electricians, often experience shoulder wear. Over time, this raises the chance of a labrum tear.
Previous Shoulder Injuries
If you had a past shoulder dislocation or fracture, the labrum is already weaker. Such shoulder injuries make future tears more likely.
Weak Shoulder Muscles
The shoulder muscles protect the joint. Weak or untrained muscles cannot support the labrum properly. This lack of strength increases the chances of injury.
Genetic and Joint Shape
Some people naturally have loose joints or shallow sockets. This posterior instability or loose fit leads to more labrum problems.
Symptoms of a Labral Tear
The symptoms of a labral tear shoulder vary, but there are some warning signs you should never ignore.
Persistent Shoulder Pain
You may feel dull or sharp pain deep inside the joint. Persistent shoulder pain is one of the most common symptoms. It increases with lifting, throwing, or even sleeping on that side.
Shoulder Instability
The shoulder may feel like it is slipping out or moving too freely. This instability makes daily tasks difficult and risky.
Motion Loss
Patients often complain of stiffness or motion loss. The shoulder cannot move as freely as before, especially during overhead motion.
Clicking or Locking Sounds
When the labrum tear catches between bones, you may hear or feel clicking, grinding, or locking during movement.
Weakness and Reduced Strength
Even simple actions like lifting a bag feel tough. This weakness happens because the labrum cannot support the upper arm properly.
Treatment Options for Labral Tears
Treatment depends on tear size, location, and symptoms. Some patients recover with simple methods, while others need surgery. Doctors decide after checking the severity and lifestyle needs.
Non-Surgical Treatments
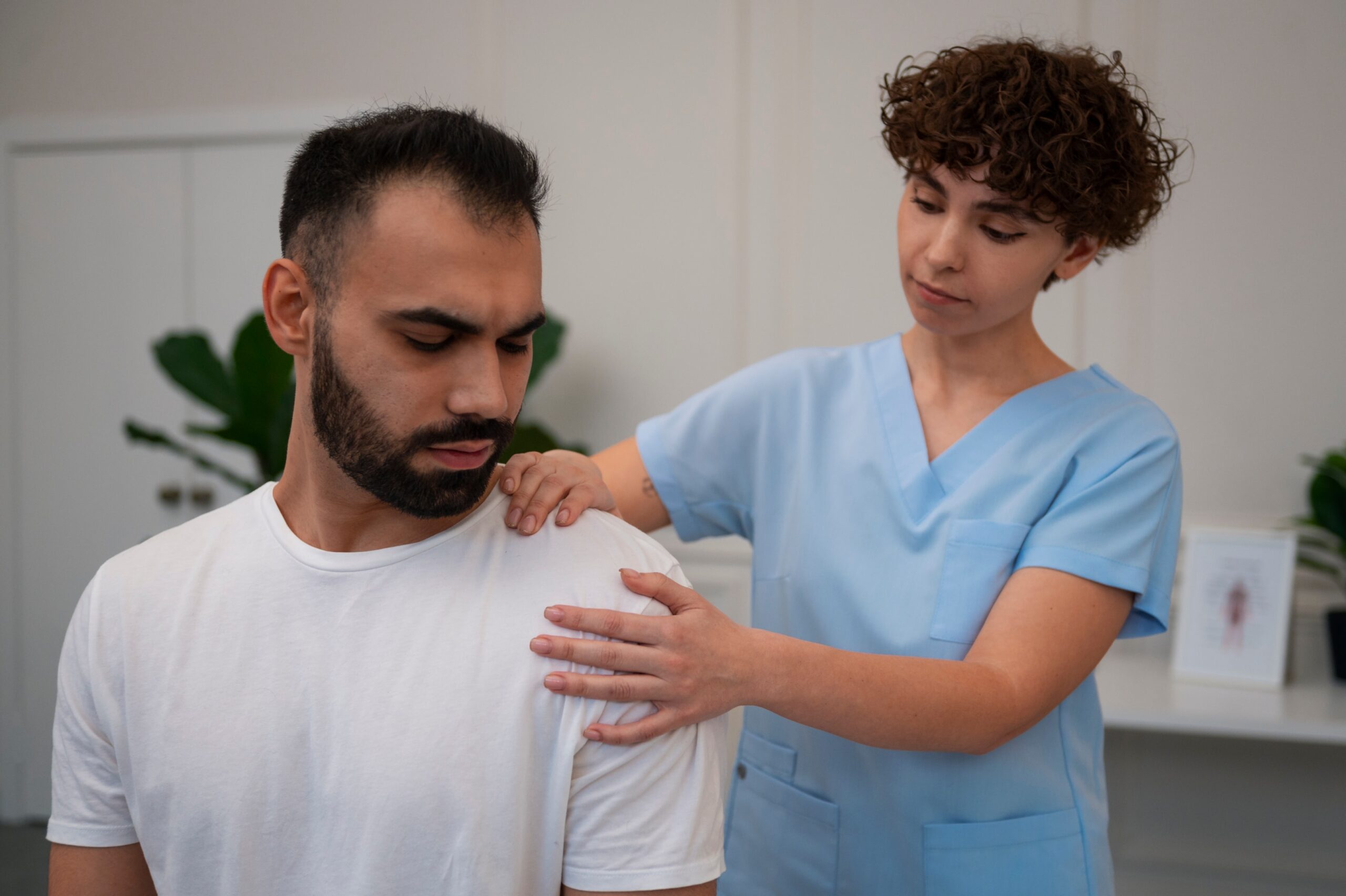
Not all labrum tears require surgery. For small tears or mild symptoms, doctors suggest nonsurgical treatment first.
- Rest and Physical Therapy: Rest reduces stress on the joint. Physical therapy builds strength in shoulder muscles and restores range of motion.
- Pain control with ice and medicines reduces swelling.
- Activity modification helps avoid motions that worsen pain.
- Guided exercises with a physical therapist improve mobility and reduce pain during daily tasks.
- These steps are helpful for patients not needing surgical treatment.
Surgical Treatments
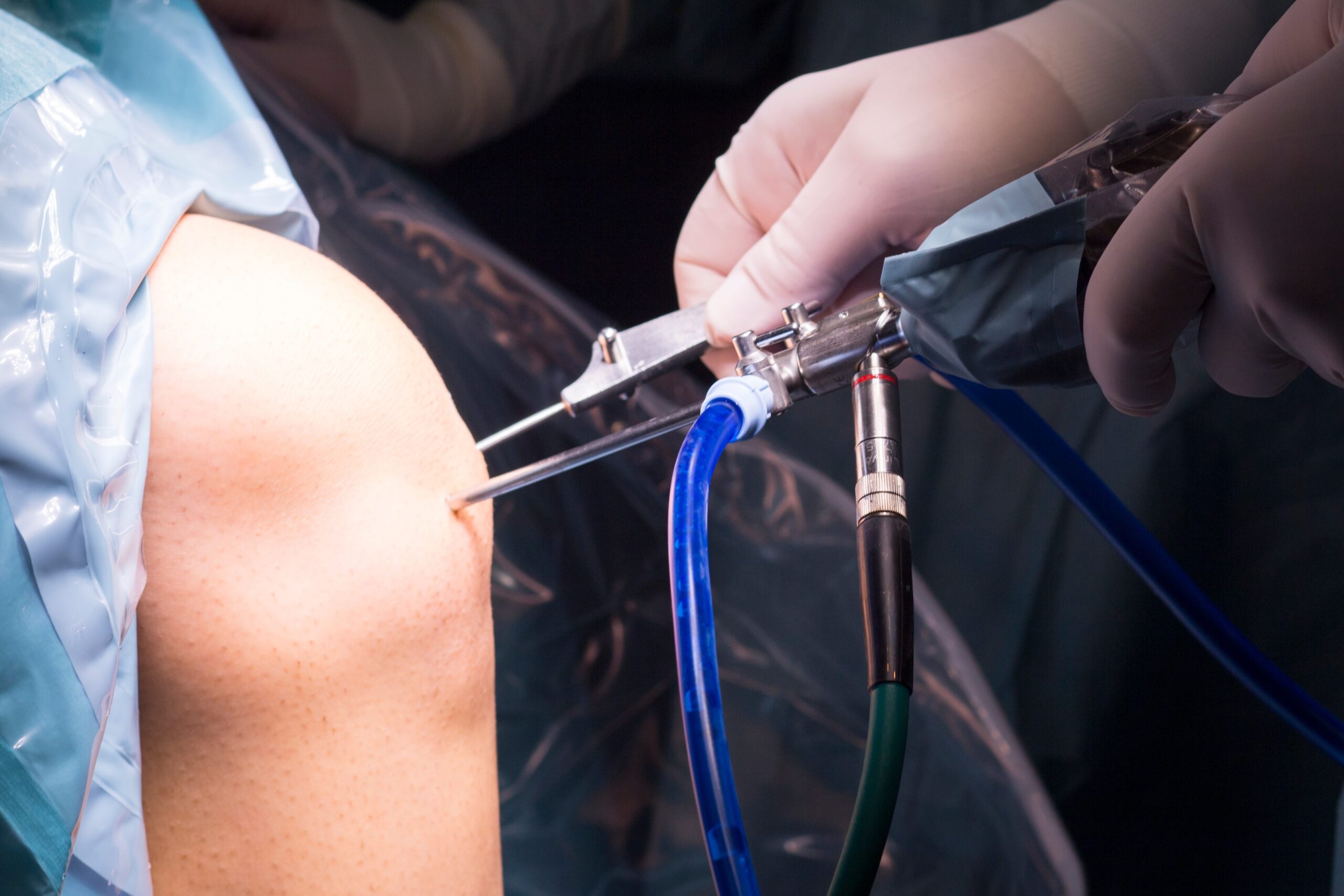
Surgical treatment is needed when symptoms do not improve or if the tear occurs after a major injury.
- Shoulder labral tear surgery is often done with arthroscopic surgery, using a small incision and special tools.
- Surgeons repair or reattach the labrum to the bone. Sometimes, they also repair the biceps tendon if it is damaged.
- Recovery needs rest, sling support, and guided physical therapy for weeks.
- Doctors may recommend surgery if instability is severe or if non-surgical care fails.
- According to the J Shoulder Elbow Surg and Orthop J Sports Med Journals, surgery success rates are high when patients follow rehab plans.
Living with a Labral Tear
A labral tear in the shoulder does not mean you must stop living. You can return to work, sports, and family duties with the right treatment.
The key is patience and proper rehab. Avoid rushing into heavy lifting or playing sports too soon. Regular exercises suggested by your physical therapist protect the labrum. Lifestyle changes like better posture and strengthening your shoulder blades and back muscles also help.
Final Thoughts
Shoulder pain should not be ignored. A shoulder labrum tear can grow worse if untreated. Knowing the causes, symptoms, and treatments makes it easier to act early.
Whether you are an athlete, worker, or homemaker, proper care ensures safe recovery and better living.
Connect with SRM Global Hospitals
At SRM Global Hospitals, patients receive the best care for labral tear shoulder treatment. With expert doctors, advanced technology, and personalised recovery plans, the hospital ensures you heal faster and return to your daily life with confidence. Whether you need rest and physical therapy or advanced surgical treatment, the specialists guide you at every step.
Book your appointment today with SRM Global Hospitals to consult with the right doctor, explore treatment options, and regain your shoulder strength.
FAQs
1. Can a labral tear shoulder heal without surgery?
Yes, small tears often improve with rest and physical therapy. Doctors usually suggest non-surgical methods before considering surgery.
2. How do I know if I have a superior labral tear?
Pain with overhead activity, clicking sounds, and weakness are common symptoms of a superior labral tear. MRI confirms the condition.
3. Is shoulder labral tear surgery safe?
Yes, most surgeries are done with arthroscopic surgery, using a small incision. Recovery takes time but success rates are high.
4. What is the difference between a bankart tear and a SLAP tear?
A bankart tear affects the lower portion of the labrum after shoulder dislocation, while slap tears affect the superior labrum anterior part where the biceps tendon attaches.
5. Can I play sports again after a labral tear shoulder treatment?
Yes, with proper rehab and guidance from a physical therapist, most patients return to playing sports safely.