Understanding Pregnancy Urine Color: Causes and What to Monitor
Pregnancy brings many changes to the body, including noticeable shifts in pregnancy urine color. Many pregnant women experience variations in urine color during pregnancy due to factors like hydration levels, diet, medications, or even potential health concerns. Tracking these changes can help ensure a healthy pregnancy.
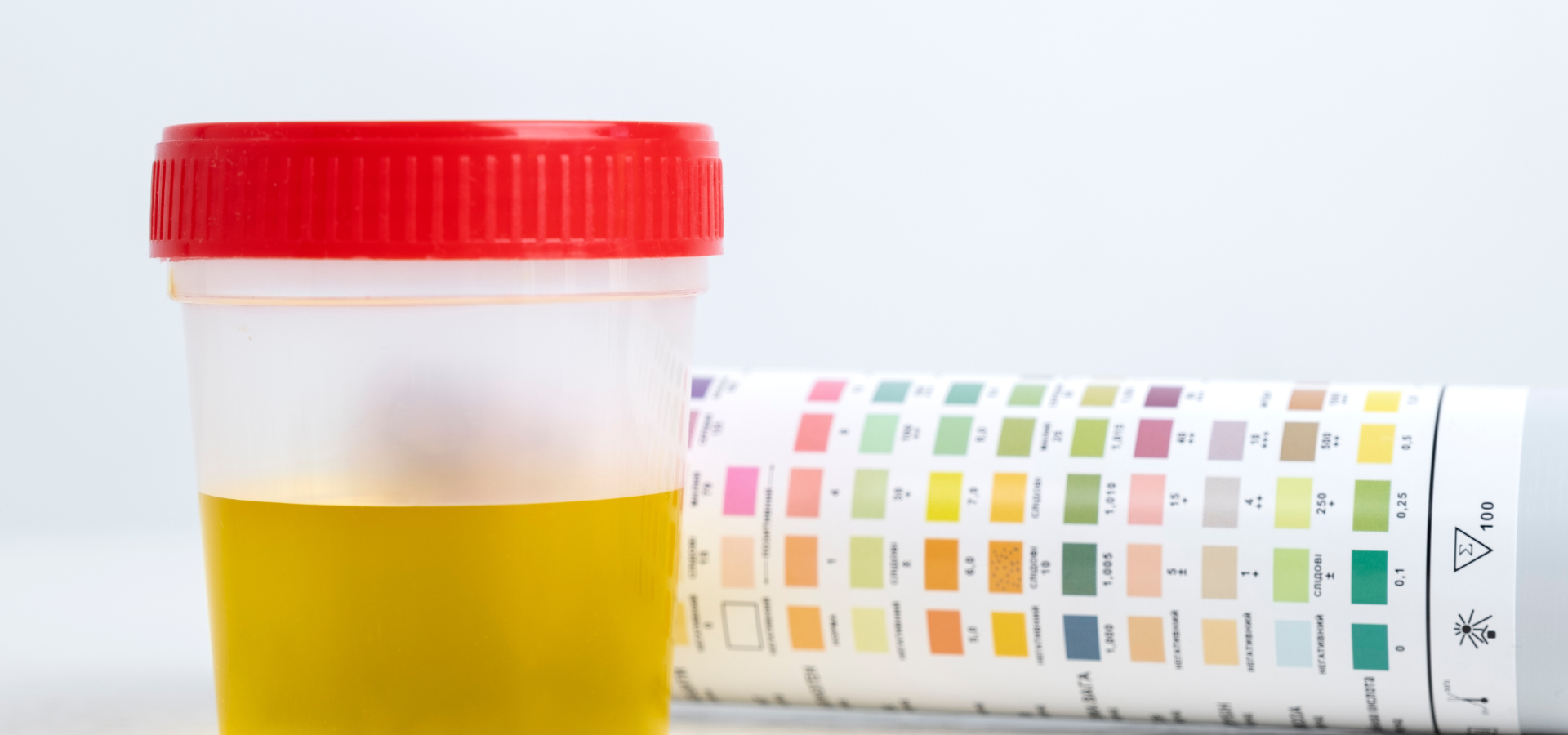
The normal urine color for pregnant women typically ranges from pale yellow to dark yellow. However, brown urine, cloudy urine, or bright yellow urine could indicate an issue. Regular urine tests help detect any abnormalities, allowing early treatment of potential problems such as urinary tract infections, kidney disease, or gestational diabetes.
Understanding changes in urine color is essential. It can reflect hydration levels, increased urine production due to pregnancy hormones, or kidney function. Recognizing what is normal and when to seek medical attention can prevent complications and ensure both the mother’s and baby’s health.
Understanding Pregnancy Urine Color: Causes and What to Monitor
Urine color changes during pregnancy are common and can be influenced by various factors, including hydration levels, diet, hormonal fluctuations, and potential medical conditions.
Many pregnant women notice shifts in urine color, ranging from pale yellow to dark yellow, orange, or even cloudy urine. While some changes are completely normal, others may indicate an underlying health issue that requires medical attention.
Common Causes of Urine Color Changes During Pregnancy
- Hydration Levels and Urine Color
One of the primary factors affecting urine color in pregnancy is hydration. When a pregnant woman is well-hydrated, her urine typically appears pale yellow or light straw-colored. However, if she is dehydrated, the urine may become dark yellow, amber, or even orange. Insufficient water intake can lead to concentrated urine, which may have a stronger odor as well. Staying hydrated is crucial for overall maternal health and fetal development, as well as preventing common pregnancy complications like urinary tract infections (UTIs) and kidney stones.
- Effect of Prenatal Vitamins on Urine Color
Many pregnant women take prenatal vitamins to support fetal growth and development. These supplements are often rich in B-complex vitamins, particularly riboflavin (vitamin B2), which can cause urine to appear bright yellow or neon yellow. While this change is generally harmless, it is essential to continue taking prenatal vitamins as prescribed to ensure proper nutrition for both mother and baby.
- Hormonal Changes and Urine Composition
Pregnancy hormones, such as human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) and progesterone, can alter urine composition, leading to slight changes in urine color. Some women may experience foamy or cloudy urine due to increased protein excretion, which is common in pregnancy. However, persistently cloudy urine may require further evaluation to rule out infections or proteinuria, a sign of preeclampsia.
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) During Pregnancy
Pregnant women are more susceptible to UTIs due to hormonal changes that slow down urine flow, increasing the risk of bacterial growth. Cloudy urine, strong-smelling urine, or dark yellow urine accompanied by a burning sensation, frequent urination, or pelvic pain could indicate a UTI. If left untreated, UTIs can lead to kidney infections or preterm labor, making early diagnosis and treatment essential.
- Kidney Function and Urine Discoloration
Kidney-related issues, including kidney disease or kidney stones, can affect urine color. If a pregnant woman notices blood-tinged urine (pink, red, or brownish urine), it could be a sign of kidney stones, a urinary tract infection, or hematuria (blood in urine). In such cases, medical consultation is necessary to determine the underlying cause and receive appropriate treatment.
- Diet, Medications, and Urine Color Changes
Certain foods and medications can also influence urine color. For example, consuming beets, carrots, or asparagus can cause urine to turn red, or orange, or have a strong odor. Similarly, some antibiotics, laxatives, and medications containing phenazopyridine can lead to orange or reddish urine. These changes are usually harmless and temporary.
Normal Urine Color During Pregnancy
The normal urine color during pregnancy typically ranges from pale yellow to dark yellow, depending on factors such as hydration levels, vitamin intake, hormonal changes, and diet. While slight variations in urine color during pregnancy are common, monitoring any drastic or persistent changes is essential for maternal and fetal health.
Factors Affecting Normal Urine Color During Pregnancy
Hydration and Urine Color
Water intake significantly impacts urine color during pregnancy. Staying well-hydrated keeps urine pale yellow or light straw-colored, indicating adequate fluid levels. Conversely, dark yellow urine often suggests dehydration, meaning the body is conserving water by producing more concentrated urine. Pregnant women should aim to drink at least 8–12 cups of water daily to maintain proper hydration and prevent urinary tract infections (UTIs) or kidney stones.
Increased Blood Volume and Urine Production
During pregnancy, blood volume increases by up to 50% to support fetal growth and maternal circulation. This increase leads to higher urine production, as the kidneys work harder to filter excess fluids and waste. As a result, some women may notice frequent urination and changes in urine concentration, causing slight fluctuations in normal urine color during pregnancy.
Hormonal Changes and Their Impact on Urine Color
Pregnancy hormones, particularly human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) and progesterone, affect how the body processes fluids and waste. These hormonal shifts may lead to mild variations in urine color, sometimes making it appear slightly darker or more concentrated. In most cases, this is harmless and part of normal pregnancy changes.
Diet and Urine Color Changes
Certain foods and beverages can temporarily alter urine color during pregnancy. For example:
- Beets, carrots, and berries may cause reddish or orange urine.
- Asparagus and coffee can give urine a strong odor.
Leafy greens and citrus fruits contribute to lighter, clear urine due to their high water content.
While these changes are temporary and not a cause for concern, it’s good to be mindful of diet-related urine discoloration.
Monitoring Urine Color During Pregnancy
A pregnant woman’s urine should generally remain within the normal urine color range. However, if urine becomes dark brown, orange, cloudy, or red or is accompanied by pain, foul odor, or foamy texture, it may indicate dehydration, a urinary tract infection (UTI), kidney issues, or even gestational diabetes. Consulting a doctor is crucial for proper evaluation and timely intervention.
Maintaining good hydration, a balanced diet and regular prenatal check-ups will help ensure urine color during pregnancy stays within a healthy range, reflecting overall maternal well-being.
Causes of Urine Color Changes
Changes in urine color can signal different conditions. Some are harmless, while others require medical attention.
Common Causes:
- Dehydration: Dark yellow urine can indicate dehydration, requiring increased fluid intake.
- Prenatal vitamins: Bright yellow urine is often caused by excess vitamin B.
- Urinary tract infection: A burning sensation and cloudy urine suggest a UTI.
- Kidney disease: Dark brown urine can indicate kidney disease or blood in the urine.
- Gestational diabetes: Changes in urine color combined with increased urine production may indicate gestational diabetes.
Monitoring these changes ensures early detection of potential health concerns.
Common Abnormalities in Urine Color
While pale yellow urine is normal, some variations may indicate an issue.
Abnormal Urine Colors and Their Possible Causes:
| Urine Color | Possible Cause |
|---|---|
| Dark yellow | Dehydration |
| Cloudy urine | Urinary tract infection |
| Brown urine | Kidney disease or blood presence |
| Bright yellow | Prenatal vitamins or vitamin B excess |
| Orange urine | Certain medications or foods |
Seeking medical attention for persistent changes helps prevent complications.
Urine Tests During Pregnancy
Urine tests are an essential part of prenatal care, helping doctors monitor a pregnant woman’s health and detect potential complications early. Throughout pregnancy, routine urinalysis is performed to identify conditions such as urinary tract infections (UTIs), kidney disease, dehydration, and gestational diabetes. Since pregnancy causes various physiological changes, regular urine tests ensure that both maternal and fetal health remain optimal.
One of the primary benefits of urine tests during pregnancy is the early detection of UTIs, which are more common due to hormonal changes that slow urine flow, increasing the risk of bacterial infections. Left untreated, UTIs can lead to kidney infections or even preterm labor. Additionally, urine tests help monitor kidney function, ensuring the body is effectively eliminating waste. Hydration levels are also assessed through urine concentration, as dehydration can lead to complications such as dizziness, swelling, and reduced amniotic fluid levels.
Another crucial function of urine tests is detecting gestational diabetes, a condition that affects blood sugar levels during pregnancy. Elevated glucose levels in urine may indicate the need for further testing and lifestyle adjustments. Overall, regular urine tests provide valuable insights into a pregnant woman’s health, ensuring timely interventions when necessary.
Monitoring Urine Health During Pregnancy
Pregnant women should monitor urine changes to detect potential problems early. Paying attention to urine color, consistency, and frequency provides insight into hydration and overall health.
Tips for Monitoring Urine Health:
- Stay hydrated to prevent dark yellow urine.
- Look for signs of urinary tract infections, such as cloudy urine.
- Regular urine tests help identify any underlying conditions.
- Consult a healthcare provider if urine color remains abnormal.
Signs of Potential Complications
Some urine color changes indicate complications. Symptoms like bloody urine, persistent dark urine, or burning sensation require immediate attention.
Warning Signs:
- Dark brown urine may indicate kidney disease.
- Blood in urine suggests a urinary tract or kidney infection.
- Frequent urination combined with increased thirst may signal gestational diabetes.
- Unusual odor or cloudy urine can indicate an infection.
Seeking medical attention at the right time prevents severe complications.
Medications and Supplements That Can Affect Urine Color
Certain medications and supplements influence urine color during pregnancy. Prenatal vitamins, antibiotics, and certain foods cause noticeable changes.
Common Causes:
- Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin): Causes bright yellow urine.
- Antibiotics: Can alter urine to orange or brown.
- Prenatal vitamins: Often cause changes in urine color.
Understanding these effects helps avoid unnecessary concern.
Maintaining a Healthy Pregnancy
A healthy pregnancy requires proper hydration, nutrition, and medical monitoring. Drinking enough water, consuming a balanced diet, and attending prenatal check-ups help maintain health.
Key Tips for Pregnant Women:
- Stay hydrated to maintain normal urine color.
- Eat a diet rich in essential nutrients.
- Perform regular urine tests to track health.
- Consult a healthcare provider for persistent urine changes.
A Healthy Pregnancy Starts with Awareness!
Pregnancy urine color serves as a health indicator. Tracking urine changes helps identify hydration levels, infections, or other medical conditions early. Regular urine tests and consultations with a healthcare provider ensure a smooth pregnancy journey.
For expert prenatal care and urine health monitoring, visit SRM Hospital today!
Conclusion
Monitoring urine health during pregnancy is crucial for ensuring both maternal and fetal well-being. Regular urine tests help detect infections, kidney function issues, dehydration, and gestational diabetes at an early stage, allowing for timely medical intervention. Changes in urine color, odor, or consistency can often signal underlying health concerns, making it essential for pregnant women to stay vigilant.
Maintaining adequate hydration, a balanced diet and regular prenatal check-ups can help keep urine color and composition within a healthy range. While slight variations are normal due to dietary and hormonal changes, persistent abnormalities such as cloudy, dark brown, or red urine should not be ignored. Consulting a doctor ensures that any potential health risks are addressed promptly.
By paying attention to urine changes and undergoing routine urine tests, pregnant women can take proactive steps toward a healthy and smooth pregnancy journey, ensuring the best possible outcome for both mother and baby.
For expert care, visit SRM Hospital and ensure a healthy pregnancy!
FAQs
1. What does dark yellow urine mean during pregnancy?
Dark yellow urine often signals dehydration. Drinking plenty of fluids helps restore normal urine color.
2. Can urine color indicate a urinary tract infection?
Yes, cloudy urine, burning sensation, or foul-smelling urine may indicate a urinary tract infection.
3. Why does pregnancy cause bright yellow urine?
Prenatal vitamins, especially vitamin B2, cause bright yellow urine due to excess nutrients being excreted.
4. How does hydration affect urine color?
Staying hydrated keeps urine pale yellow, while dehydration makes urine dark yellow.
5. When should I seek medical attention for urine changes?
If urine turns dark brown, bloody, or cloudy for an extended period, seek medical attention immediately.