Role of Angiography in Diagnosing Heart Disease
Heart diseases are making headlines with the rise in the number of heart attacks reported by young adults. Most of these could have been averted if the patient had chosen to get a routine or timely cardiac check-up. Regular full body assessment and cardiac checkups can help to detect any signs of disease.
What is angiography?
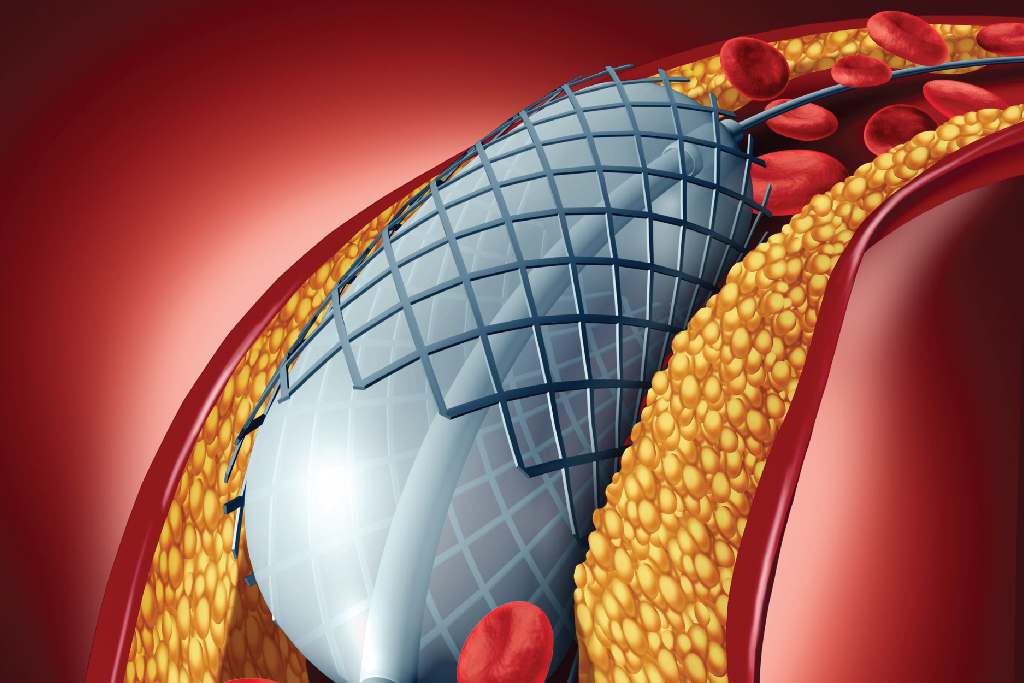
Angiography is an investigation similar to an X-ray and used to detect any blockages in the blood vessels of the heart. It can detect abnormalities such as artery narrowing, vessel bulging, and vessel blockages. This test is an essential component of the diagnostic procedures providing detailed images that help in the early detection and treatment of heart disease.
How is angiography performed ?
- Sedation and Preparation: You may be given a sedative to help you relax, but you will remain awake during the surgery.
- Incision: A small incision will be made across one of the arteries near your wrist or groin.
- Anaesthesia and Catheter Insertion: Local anaesthesia is used to numb the area around the incision, and a thin, flexible tube (catheter) is placed into the artery.
- Contrast Agent Injection: An X-ray sequence is obtained while the contrast agent (dye) flows through your blood vessels after being injected through the catheter.
- Duration: The exam may last up to two hours. A few hours later, you should be able to return home.
Angiography, Angioplasty, and Angiogram
Angiography is an investigative procedure that enables the doctor to closely examine the blood vessels using X-rays and check for blocked or narrowed arteries. Angioplasty is a procedure performed to broaden the blood vessels. The medical name for this procedure is catheter angiogram.
What can be detected through an angiography procedure?
People with a family history of coronary artery disease have a higher probability of developing heart-disease; so they are advised to undergo the procedure so that the cardiologist can check for any sign of cardiac problems. Patients who experience vague chest pain also undergo this diagnostic procedure. Based on the test results, the cardiologist may diagnose any one or more of the following:
- Blocked coronary arteries
- Heart failure
- Aneurysms
- Atherosclerosis
- Coronary artery disease
- Pulmonary embolism
Advantages of Angiography
- Angiography offers clear images of blood arteries, detecting blockages, narrowing, and abnormalities. This level of information is critical for detecting a variety of disorders, especially coronary artery disease (CAD).
- High-resolution images from an angiography procedure aid in proper diagnosis of cardiovascular problems. This accuracy aids in determining the precise position and severity of the disorders, resulting in more successful treatment approaches.
- Angiography provides real-time imaging of blood flow and vascular conditions. This real-time element is especially useful during interventional treatments such as angioplasty or stent implantation, as it aids the clinician in making accurate modifications.
- Angiography is a less invasive procedure than surgical techniques. This shortens the recovery time and lowers the likelihood of problems associated with more intrusive surgeries.
- Angiography is a versatile tool that makes it a useful tool for diagnosing a wide spectrum of cardiovascular diseases.
- This procedure provides a full assessment of the cardiovascular system. It not only detects blockages but also evaluates the general health of the blood arteries, aiding in the diagnosis of aneurysms, congenital malformations, and other vascular abnormalities.
- Angiography is essential for interventional procedures like angioplasty and stent implantation. It helps cardiologists navigate blood channels and accurately implant devices for treating blockages.
- Angiography is useful for both preoperative planning and post-operative evaluation. It aids in surgical planning by providing detailed pictures of the blood vessels and assessing the efficacy of surgical operations postoperatively.
- Angiography improves patient outcomes by allowing early and accurate identification of cardiovascular illnesses. Early detection enables timely intervention, which can prevent disease progression and lower the risk of serious consequences like heart attacks or strokes.
- Recent improvements in angiography technology, including DSA, MRA, and CTA, have improved the diagnostic tool. These improvements improve image clarity, limit radiation exposure, and provide alternate treatment alternatives for patients with specific health issues.
Angiography has several benefits for the detection and treatment of cardiovascular and other vascular illnesses. The capability to give precise, real-time views of blood arteries leads to more accurate diagnosis and effective treatment strategies, resulting in better patient outcomes. The procedure’s minimally invasive nature, adaptability, and technological developments all contribute to its usefulness as a crucial diagnostic tool in modern medicine.