Managing Heart Rate High After Eating: Causes and Solutions
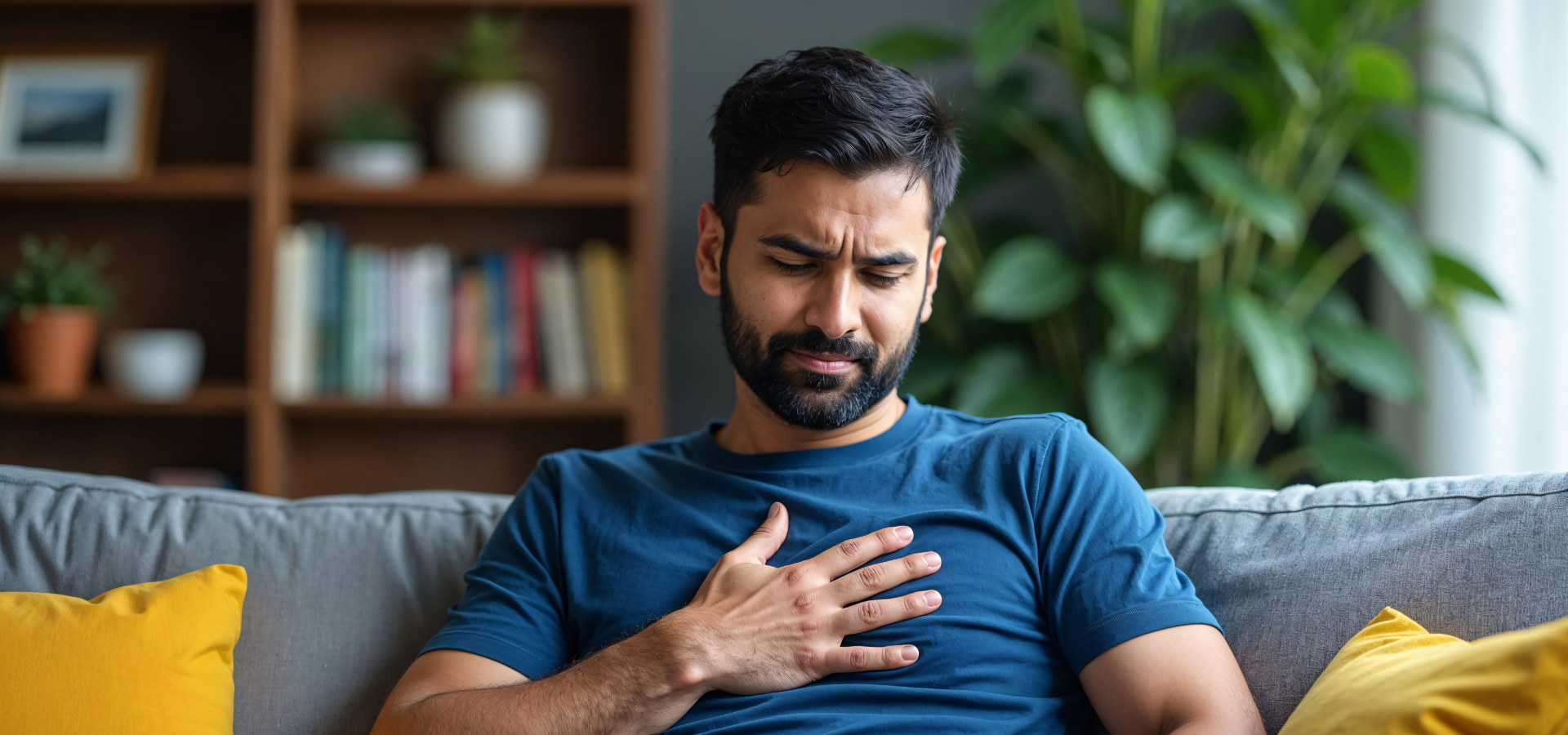
Experiencing heart rate high after eating is a common occurrence for many individuals. While occasional episodes may not be a cause for concern, frequent or intense palpitations can indicate an underlying issue that requires attention. This condition, often referred to as heart palpitations after eating, can range from a mild fluttering sensation in the chest to a rapid or irregular heartbeat that may interfere with daily activities.
Several factors, including spicy foods, high blood pressure, low blood sugar, or digestive issues, can contribute to these palpitations. In some cases, conditions like atrial fibrillation or other cardiovascular issues may be involved.
Understanding what triggers heart palpitations and adopting lifestyle changes, such as adjusting diet and hydration, is key to managing symptoms. Seeking medical guidance when heart palpitations occur frequently or alongside other symptoms like dizziness or chest pain is crucial for ensuring overall cardiovascular health and well-being.
Understanding Heart Palpitations
Heart palpitations refer to sensations of an unusually fast or irregular heartbeat. Individuals may feel these heart palpitations in their chest, throat, or neck, often becoming more aware of their heart’s activity. While occasional heart palpitations can be a normal reaction to certain stimuli, frequent episodes may require medical attention.
The heart is composed of four chambers; the upper chambers, or atria, receive blood, while the lower chambers, or ventricles, pump blood out. Heart palpitations after eating may be felt when there’s a disruption in this cycle, causing the heart to beat abnormally.
Eating can sometimes trigger heart palpitations, especially if the meal is large, high in carbohydrates, or contains stimulants such as caffeine. These heart palpitations can also indicate atrial fibrillation, a common type of abnormal heart rhythm. While it’s normal to notice your heart rate high after eating, persistent or severe heart palpitations could indicate an underlying condition.
Causes of Heart Palpitations After Eating
Identifying the triggers of heart palpitations after eating is the first step toward management and treatment. Various factors, ranging from dietary choices to underlying medical conditions, can influence blood pressure and cardiovascular health after meals.
Certain ingredients such as caffeine intake, energy drinks, sugar, and spicy foods can significantly trigger heart palpitations. Additionally, processed foods high in sodium or unhealthy fats can contribute to heart palpitations after eating.
Medical conditions like high blood pressure, low blood sugar, and heart disease can exacerbate heart palpitations. Certain medications, including over-the-counter drugs, can also increase heart rate high after eating.
Trigger Foods and Substances
Diet plays a pivotal role in managing heart palpitations. Avoiding specific foods and substances can help stabilize blood pressure and minimize discomfort.
Caffeine intake:
Found in coffee, tea, and energy drinks, caffeine is a major stimulant that can increase heart rate high after eating.
Sugar spikes:
High-sugar foods can cause blood sugar fluctuations, leading to heart palpitations.
Spicy foods:
These can stimulate the nervous system, increasing heart palpitations after eating.
Alcohol consumption:
Drinking alcohol can affect the heart’s rhythm and lead to episodes of heart palpitations.
Medical Conditions and Hormonal Changes
Heart palpitations after eating can be triggered by underlying medical conditions and hormonal fluctuations. While occasional palpitations may not indicate a severe issue, frequent episodes may point to an underlying heart condition or significant hormonal imbalance that affects cardiovascular health. Understanding these factors is essential for effective management and prevention.
Underlying Heart Conditions
Several cardiovascular conditions can make individuals more prone to heart palpitations after eating. One of the most common is cardiomyopathy, a disease of the heart muscle that affects its ability to pump blood efficiently. When the heart muscle becomes enlarged, thickened, or stiff, it can struggle to handle increased blood flow after meals, triggering palpitations.
Another condition, coronary artery disease (CAD), occurs when plaque builds up in the arteries, restricting blood flow. When digestion requires extra blood supply, the heart has to work harder, increasing the risk of palpitations. Atrial fibrillation, a type of abnormal heart rhythm, can also be aggravated after eating, especially in individuals with high blood pressure.
Certain medical conditions such as diabetes can indirectly contribute to palpitations due to fluctuating blood sugar levels. Acid reflux (GERD) is another possible cause, as irritation of the esophagus can stimulate the vagus nerve, which plays a role in heart rate regulation.
Hormonal Influences
Hormonal imbalances can significantly affect heart function. Women, particularly those going through menopause or pregnancy, often experience palpitations due to fluctuating levels of estrogen and progesterone. These hormonal changes can cause the blood vessels to widen, lowering blood pressure and making the heart beat faster to compensate.
Hot flashes during menopause may also contribute to heart palpitations, as the sudden rise in body temperature can trigger an increased heart rate. Similarly, thyroid imbalances, particularly hyperthyroidism, can lead to irregular or rapid heartbeats after meals.
Managing these conditions with appropriate medical care, dietary adjustments, and stress reduction techniques can help minimize palpitations and improve cardiovascular health.
Managing Heart Palpitations
Managing heart palpitations involves a combination of dietary adjustments, lifestyle changes, and sometimes medication. Opting for a balanced diet rich in lean proteins, whole grains, and vegetables can help stabilize heart rate high after eating. Avoiding spicy foods, processed foods, and energy drinks is crucial in managing heart palpitations after eating.
Engaging in deep breathing exercises and stress management techniques can significantly reduce heart palpitations. Activities such as meditation, yoga, and bowel movement regulation also contribute to better overall cardiovascular health.
Dietary Strategies
Maintaining a heart-healthy diet is one of the most effective ways to manage heart palpitations after eating. The right balance of nutrients can help regulate blood sugar levels, prevent sudden spikes in blood pressure, and support overall cardiovascular health. Many people experience heart rate high after eating due to food-related triggers, but by making thoughtful dietary adjustments, these episodes can be significantly reduced.
A heart-healthy diet should include lean proteins, whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats. These foods provide essential nutrients while keeping the heart functioning optimally. Processed foods, on the other hand, are often high in sodium, unhealthy fats, and additives that may trigger heart palpitations. Reducing the intake of these foods can lower the risk of experiencing irregular heartbeat and help maintain a steady heart rate.
Hydration plays a crucial role in stabilizing heart palpitations after eating. Dehydration can lead to electrolyte imbalances, which affect the heart’s electrical activity. Drinking adequate water throughout the day, especially after consuming caffeine, alcohol, or salty foods, helps regulate blood pressure and maintain a normal heartbeat. On the other hand, excessive alcohol consumption can dehydrate the body and cause heart palpitations by interfering with the heart’s electrical signals.
Spicy foods are another common trigger for eating heart palpitations. While capsaicin, found in chili peppers, has health benefits, it can also stimulate the nervous system and cause a temporary increase in heart rate. Those sensitive to spicy foods should consider limiting their intake to avoid unnecessary palpitations.
Refined sugar and high-carb meals can cause rapid fluctuations in blood sugar, leading to an overstimulated nervous system and an increased risk of heart palpitations. To prevent this, meals should be balanced with complex carbohydrates, fiber, and protein to ensure a gradual release of energy rather than a sudden spike.
By making dietary changes, including choosing nutrient-rich foods, staying hydrated, and avoiding known trigger foods, individuals can better manage heart palpitations and promote overall cardiovascular health. Making these lifestyle adjustments can also reduce the need for certain medications and enhance long-term heart health.
Relaxation Techniques
Stress management techniques such as deep breathing exercises and physical activity can help prevent heart palpitations. Engaging in lifestyle changes like regular exercise and proper hydration can contribute to overall cardiovascular health.
When to Seek Medical Advice
It is important to consult a healthcare provider if heart palpitations after eating become frequent or are accompanied by symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or dizziness. Persistent heart palpitations could indicate heart disease or abnormal heart rhythm, which require further medical evaluation.
Stopping Palpitations Immediately
In moments of discomfort, several techniques can help manage heart palpitations after eating:
- Cold compress: Applying a cold towel to the face can help slow heart palpitations.
- Vagal maneuvers: Techniques such as holding your breath and bearing down can help regulate blood pressure and heart rhythm.
Preventing Future Episodes
Identifying trigger palpitations and making lifestyle changes can help prevent heart palpitations after eating. Practicing deep breathing exercises and avoiding high blood pressure medications that may trigger heart palpitations is key to maintaining overall cardiovascular health.
Final Thoughts
Experiencing heart palpitations after eating can be alarming, but with the right approach, they can be managed effectively. Individuals can significantly reduce heart palpitations by maintaining a heart-healthy diet, staying hydrated, and avoiding known trigger palpitations.
Engaging in lifestyle changes and consulting a healthcare provider when necessary ensures long-term cardiovascular health.
If you’re experiencing heart palpitations after eating, visit SRM Hospital for a comprehensive evaluation and personalized treatment plan.
FAQs
1. What foods should I avoid to prevent heart palpitations?
Avoid caffeine, spicy foods, and alcohol consumption to reduce heart palpitations.
2. Can dehydration cause heart palpitations?
Yes, dehydration can lead to low blood sugar, increasing the risk of heart palpitations after eating.
3. Are heart palpitations dangerous?
While often harmless, frequent heart palpitations may signal heart disease and require medical attention.
4. How can I stop heart palpitations immediately?
Applying a cold compress, engaging in deep breathing exercises, or practicing vagal maneuvers can help.
5. When should I see a doctor for heart palpitations?
If heart palpitations occur frequently with chest pain or other symptoms, consult a healthcare provider immediately.